A Heap (aka a Priority Queue) is a data structure that (most commonly) uses a complete binary tree stored in an array, and maintains the heap property so you can repeatedly access the smallest or largest item efficiently.
Core idea
Two rules define a binary heap:
- Complete binary tree: filled level-by-level, left-to-right (last level can be partially filled).
- Heap property:
A heap is not fully sorted (unlike a BST). It only guarantees ordering between parent and children.
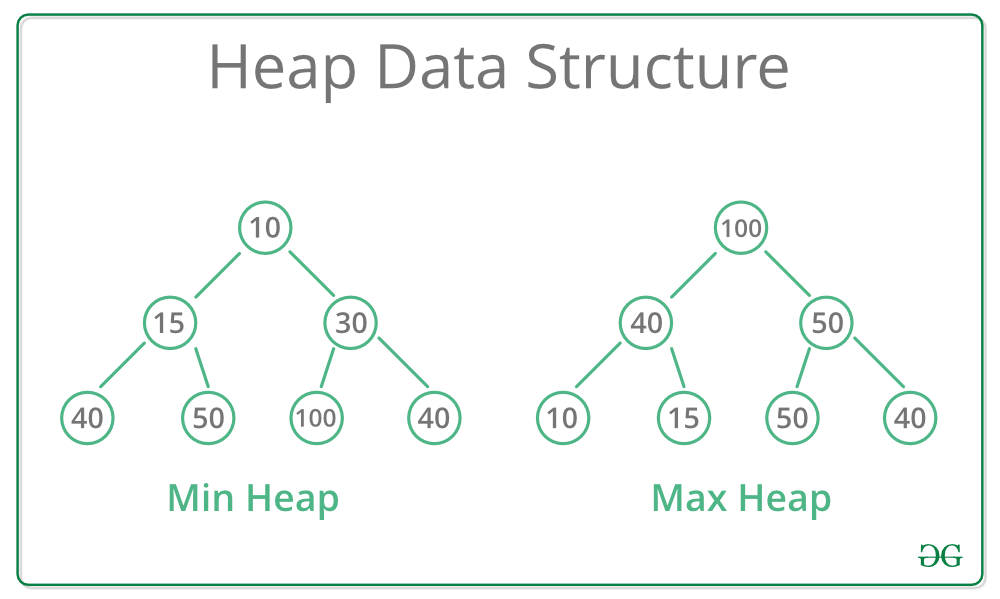
Array representation (why heaps are practical)
Heaps are usually stored in an array A:
parent(i) = (i - 1) // 2left(i) = 2*i + 1right(i) = 2*i + 2
This works because the structure is always “complete,” so the tree shape is implicit.
Operations + intuition
-
Peek: return the top element (
A[0])- Time:
O(1)
- Time:
-
Insert (push):
- append new item to end (keeps completeness)
- sift up: while it violates heap property, swap with parent
- Time:
O(log n)
-
Pop (extract min/max):
- remove the root (this is the answer)
- move last element to root
- sift down: swap down with the appropriate child until heap property returns
- Time:
O(log n)
Quick example (min-heap)
Start: [2, 5, 3] (valid min-heap)
Insert 1:
- append →
[2, 5, 3, 1] - sift up: swap with 5 →
[2, 1, 3, 5] - sift up: swap with 2 →
[1, 2, 3, 5]
Pop:
- remove root
1, move last to root →[5, 2, 3] - sift down: swap with 2 →
[2, 5, 3]
Heapify + build heap (common confusion)
-
Heapify (sift-down at an index): fix heap property starting from a node, pushing it down
- Time:
O(log n)
- Time:
-
Build heap from an array (what Python
heapq.heapifydoes): transform an unsorted array into a heap- Time:
O(n) - Extra space:
O(1)(in-place)
- Time:
Heap sort (clarified)
Heap sort is: build a heap, then pop repeatedly to produce sorted output.
- Build heap:
O(n) - Pop
ntimes:O(n log n) - Total:
O(n log n)
(Heaps don’t “heap sort after every pop” — each pop is just O(log n) restructuring.)
Python patterns (heapq)
import heapq
from collections import Counter
from itertools import count
# -----------------------------
# Min-heap basics
# -----------------------------
A = [1, 4, 2, 21, 1, 4]
heapq.heapify(A) # O(n)
top = A[0] # peek, O(1)
heapq.heappush(A, 4) # push, O(log n)
minn = heapq.heappop(A) # pop min, O(log n)
# -----------------------------
# Heap sort (ascending)
# Time: O(n log n), Space: O(n) for output
# -----------------------------
def heapsort(arr):
h = arr[:] # copy if you want to preserve arr
heapq.heapify(h)
return [heapq.heappop(h) for _ in range(len(h))]
# -----------------------------
# Max-heap in Python (negation trick)
# -----------------------------
nums = [5, 1, 7, 3]
max_heap = [-x for x in nums]
heapq.heapify(max_heap)
maxx = -heapq.heappop(max_heap)
heapq.heappush(max_heap, -10)
# -----------------------------
# Priority queue: tuples sort left-to-right
# (priority, value)
# -----------------------------
pq = []
heapq.heappush(pq, (2, "medium"))
heapq.heappush(pq, (1, "urgent"))
priority, value = heapq.heappop(pq) # (1, "urgent")
# -----------------------------
# If value types might not be comparable, use a tie-breaker
# (priority, tie, value)
# -----------------------------
tie = count()
safe = []
heapq.heappush(safe, (1, next(tie), {"job": "x"}))
heapq.heappush(safe, (1, next(tie), {"job": "y"}))
_, _, item = heapq.heappop(safe)
# -----------------------------
# Frequency heap: (count, key)
# -----------------------------
D = ["a", "b", "a", "c", "b", "a"]
counter = Counter(D)
freq_heap = []
for k, c in counter.items():
heapq.heappush(freq_heap, (c, k))Key interview Uses
- Top K: keep a min-heap of size
K - Kth largest: same idea; root is answer after processing
- Dijkstra / A*: min-heap prioritized by current shortest distance
- Merge K sorted lists: heap of current heads
Complexity Cheat Sheet
| Operation | Time | Extra Space |
|---|---|---|
| Peek | O(1) | O(1) |
| Push | O(log n) | O(1) |
| Pop | O(log n) | O(1) |
Build heap from array (heapify) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Heap sort (pop n times) | O(n log n) | O(n) if output list |
Linked Map of Contexts